MOTION DETECTOR PROJECT
Introduction
[nextpage title=”Introduction” ]
A 3-axis accelerometer sits at the heart of this project to provide a nifty little motion detector.
An electronic motion detector contains an optical, microwave, or acoustic sensor, and in many cases a transmitter for illumination. However, a passive sensor only senses a signal emitted by the moving object itself. Changes in the optical, microwave, or acoustic field in the device’s proximity are interpreted by the electronics based on one of the technologies listed below. Most inexpensive motion detectors can detect up to distances of at least 15 feet (5 meters). Specialized systems are more expensive but have much longer ranges. Tomographic motion detection systems can cover much larger areas because the radio waves are at frequencies which penetrate most walls and obstructions, and are detected in multiple locations, not just at the location of the transmitter.
Parts Required
- Freetronics Eleven or any compatible Arduino
- Freetronics 3-Axis Accelerometer Module
- Male header pins
- Seeed Studio’s Grove Base Shield
- Seeed Studio’s Universal Cables
- Seeed Studio’s Grove Button
- Seeed Studio’s Grove Buzzer
- Mini Breadboard 4.5cm x 3.5cm
- Protoshield and female header pins
- 1 x LED
- 330 ohm resistor
- Wires
- 9V Battery + Battery Clip
Instructions
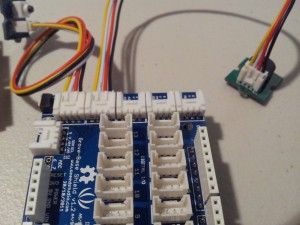
- Overlay the Seeed Studio Base Shield onto the Freetronics Eleven (or compatible Arduino).
- Use a Universal Cable to attach a Seeed Studio Grove Button to Analog Pin 0 on the Base Shield. The socket is located directly above the Freetronics Eleven Power plug, and next to the Reset button on the Base Shield. Please note that Analog Pin 1 is not used by the Grove Button.
- Use a universal Cable to attache a Seeed Studio Grove Buzzer to Analog Pin 1 on the Base Shield. This is the socket next to the one used in Step 2.
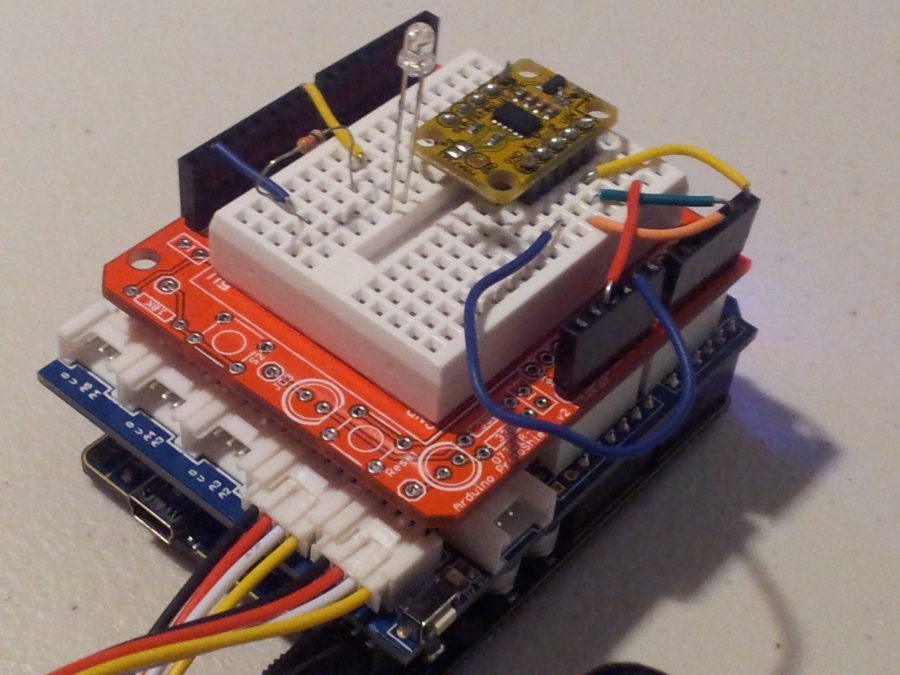
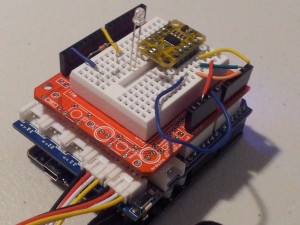
- Solder the female header pins to the Protoboard. Overlay the protoboard onto the Base Shield to create a third layer. I created this layer to tidy up the project and make it a little bit more portable. You could just wire up another breadboard on the side.
- Stick a mini-breadboard (4.5cm x 3.5cm) onto the protoboard. This allows you to use the protoboard for other projects.
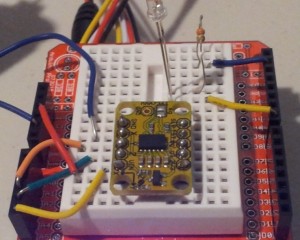
- Solder the male headers to the 3-axis accelerometer, and then place it centrally onto the breadboard.
- You need 5 wires to connect:
- GND on protoboard to GND on accelerometer
- 5V on protoboard to VIN on accelerometer
- Analog Pin 3 on protoboard to X on accelerometer
- Analog Pin 4 on protoboard to Y on accelerometer
- Analog Pin 5 on protoboard to Z on accelerometer
- Connect digital pin 8 to an LED and 330 ohm resistor on the breadboard,
- Use a wire to connect the resistor mentioned above to GND on the protoboard
- Connect the USB cable from your computer to the Freetronics Eleven, and upload the Arduino Sketch to the board.
- Disconnect the USB cable, and then power the Freetronics Eleven using a 9V battery and clip.
- When you press the button, it will sound 3 warning sounds before it becomes activated.
- If it detects a vibration or motion that exceeds the tolerance level, it will alarm. The alarm will continue until you either press the Grove button – which resets and reactivates the device or you can press the Reset button on the Base Shield to Stop monitoring for motion.
[/nextpage]
Sketch[nextpage title=”Sketch” ]
[/nextpage]
Arduino code[nextpage title=”Arduino code” ]
//Motion Detector Alarm
//Global Variables and constants
const int buttonPin = A0; // button Pin connected to Analog 0
const int buzzerPin = A1; // buzzer Pin connected to Analog 1
//Accelerometer Pins
const int x = A3; // X pin connected to Analog 3
const int y = A4; // Y pin connected to Analog 4
const int z = A5; // Z pin connected to Analog 5
//Alarm LED
const int ledPin = 8; // LED connected to Digital 8
int tolerance=20; // Sensitivity of the Alarm
boolean calibrated=false; // When accelerometer is calibrated - changes to true
boolean moveDetected=false; // When motion is detected - changes to true
//Accelerometer limits
int xMin; //Minimum x Value
int xMax; //Maximum x Value
int xVal; //Current x Value
int yMin; //Minimum y Value
int yMax; //Maximum y Value
int yVal; //Current y Value
int zMin; //Minimum z Value
int zMax; //Maximum z Value
int zVal; //Current z Value
void setup(){
//Begin Serial communication
Serial.begin(38400);
//Initilise LED Pin
pinMode(ledPin, OUTPUT);
}
void loop(){
// If the button is pressed, initialise and recalibrate the Accelerometer limits.
if(analogRead(buttonPin)>500){
calibrateAccel();
}
// Once the accelerometer is calibrated - check for movement
if(calibrated){
if(checkMotion()){
moveDetected=true;
}
}
// If motion is detected - sound the alarm !
if(moveDetected){
Serial.println("ALARM");
ALARM();
delay(1000);
}
}
//This is the function used to sound the buzzer
void buzz(int reps, int rate){
for(int i=0; i<reps; i++){
analogWrite(buzzerPin,900);
delay(100);
analogWrite(buzzerPin,0);
delay(rate);
}
}
// Function used to calibrate the Accelerometer
void calibrateAccel(){
// reset alarm
moveDetected=false;
//initialise x,y,z variables
xVal = analogRead(x);
xMin = xVal;
xMax = xVal;
yVal = analogRead(y);
yMin = yVal;
yMax = yVal;
zVal = analogRead(z);
zMin = zVal;
zMax = zVal;
// Calibration sequence initialisation sound - 3 seconds before calibration begins
buzz(3,1000);
//calibrate the Accelerometer (should take about 0.5 seconds)
for (int i=0; i<50; i++){
// Calibrate X Values
xVal = analogRead(x);
if(xVal>xMax){
xMax=xVal;
}else if (xVal < xMin){
xMin=xVal;
}
// Calibrate Y Values
yVal = analogRead(y);
if(yVal>yMax){
yMax=yVal;
}else if (yVal < yMin){
yMin=yVal;
}
// Calibrate Z Values
zVal = analogRead(z);
if(zVal>zMax){
zMax=zVal;
}else if (zVal < zMin){
zMin=zVal;
}
//Delay 10msec between readings
delay(10);
}
//End of calibration sequence sound. ARMED.
buzz(3,40);
printValues(); //Only useful when connected to computer- using serial monitor.
calibrated=true;
}
//Function used to detect motion. Tolerance variable adjusts the sensitivity of
movement detected.
boolean checkMotion(){
boolean tempB=false;
xVal = analogRead(x);
yVal = analogRead(y);
zVal = analogRead(z);
if(xVal >(xMax+tolerance)||xVal < (xMin-tolerance)){
tempB=true;
Serial.print("X Failed = ");
Serial.println(xVal);
}
if(yVal >(yMax+tolerance)||yVal < (yMin-tolerance)){
tempB=true;
Serial.print("Y Failed = ");
Serial.println(yVal);
}
if(zVal >(zMax+tolerance)||zVal < (zMin-tolerance)){
tempB=true;
Serial.print("Z Failed = ");
Serial.println(zVal);
}
return tempB;
}
// Prints the Sensor limits identified during Accelerometer calibration.
// Prints to the Serial monitor.
void printValues(){
Serial.print("xMin=");
Serial.print(xMin);
Serial.print(", xMax=");
Serial.print(xMax);
Serial.println();
Serial.print("yMin=");
Serial.print(yMin);
Serial.print(", yMax=");
Serial.print(yMax);
Serial.println();
Serial.print("zMin=");
Serial.print(zMin);
Serial.print(", zMax=");
Serial.print(zMax);
Serial.println();
Serial.println("------------------------");
}
//Function used to make the alarm sound, and blink the LED.
void ALARM(){
//don't check for movement until recalibrated again
calibrated=false;
// sound the alarm and blink LED
digitalWrite(ledPin, HIGH);
buzz(4,20);
digitalWrite(ledPin, LOW);
}











Post Comment
You must be logged in to post a comment.