Braking System and Its Classification, Application, Advantages and Disadvantages
-
Classification of Brakes
- INTRODUCTION
Requirements of braking system:
- decelerate in a controlled repeatable manner
- help maintain constant speed down hill
- hold vehicle stationary on a flat or on a gradient
-
Definition of Brakes
“The kinetic energy due to motion of the vehicle is dissipated in the form of heat energy due to friction between moving parts (wheel or wheel drum) and stationary parts of vehicle (brake shoes)”.
Baking system is necessary in an automobile for stopping the vehicle. Brakes are applied on the wheels to stop or to slow down the vehicle.
-
Functions of Brakes
There are two main functions of brakes :
- To slow down or stop the vehicle in the shortest possible time at the time of need.
- To control the speed of vehicle at turns and also at the time of driving down on a hill slope.
-
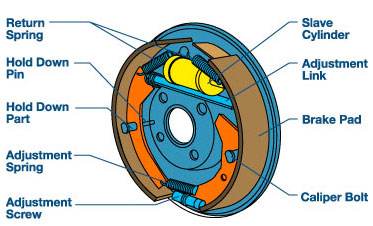
CLASSIFICATION OF BRAKES
On the Basis of Method of Actuation
(a) Foot brake (also called service brake) operated by foot pedal
In the Automobile Engineering a brake operated by applying pressure to a foot pedal then it is called foot brake.
(b) Hand brake – it is also called parking brake operated by hand
Parking brakes or emergency brakes are essentially mechanical brakes operated by hand. These are used to prevent the motion of vehicle when parked at a place or when parked on slopes. In cars, these brakes are generally attached to rear wheels. In this type, a cable connects the hand lever to the brake. Brakes are applied by pulling the lever and released by pushing a button (provided on lever) and pressing the lever down.
On the Basis of Mode of Operation
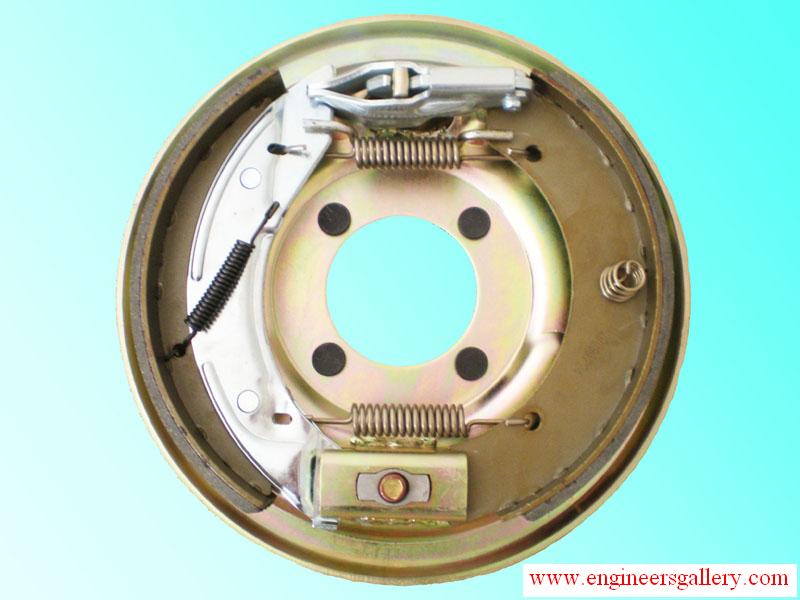
Internal expanding shoe brakes are most commonly used in automobiles. In an automobile, the wheel is fitted on a wheel drum. The brake shoes come in contact with inner surface of this drum to apply brakes.
(b) Hydraulic brakes
The brakes which are actuated by the hydraulic pressure (pressure of a fluid) are called hydraulic brakes. Hydraulic brakes are commonly used in the automobiles.
(c) Air brakes
Air brakes are applied by the pressure of compressed air. An Air pressure applies force on brakes shoes through suitable linkages to operate brakes. An air compressor is used to compress air. This compressor is run by engine power.
(d) Vacuum brakes
Vacuum brakes are a piston or a diaphragm operating in a cylinder. For application of brakes one side of piston is subjected to atmospheric pressure while the other is applied vacuum by exhausting air from this side. A force acts on the piston due to difference of pressure. This force is used to operate brake through suitable linkages.
(e) Electric brakes
In electrical brakes an electromagnet is used to actuate a cam to expand the brake shoes. The electromagnet is energized by the current flowing from the battery. When flow of current is stopped the cam and brake shoes return to their original position and brakes are disengaged. Electric brakes are not used in automobiles as service brakes.
On the Basis of Action on Front or Rear Wheels
Disc Brake is mostly usage in Front Wheel Brakes.
Drum Brake is usage in Rear Wheel Brakes.
On the Basis of Method of Application of Braking Contact
(a) Internally – expanding brakes
(b) Externally – contracting brakes
-
Application of Brakes
When brake pedal is pressed to apply the brakes, the piston in the master cylinder forces the brake fluid. This increases the pressure of fluid. This pressure is transmitted in all the pipes and upto all wheel cylinders according to Pascal’s law. This increased pressure forces out the two pistons in the wheel cylinders. These pistons are connected to brake shoes. So, the brake shoes expand out against brake drums. Due to friction between brake linings and drum, wheels slow down and brakes are applied.
-
ADVANTAGES AND DISADVANTAGES OF HYDRAULIC BRAKES
Advantages
- Equal braking action on all wheels.
- Increased braking force.
- Simple in construction.
- Low wear rate of brake linings.
- Flexibility of brake linings.
- Increased mechanical advantage.
Disadvantages
- Whole braking system fails due to leakage of fluid from brake linings.
- Presence of air inside the tubing’s ruins the whole system.











Post Comment
You must be logged in to post a comment.