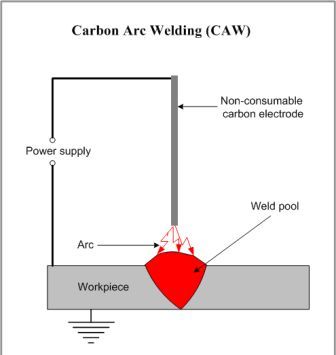
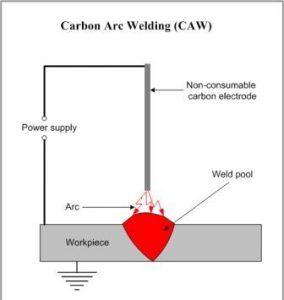
Carbon Arc Welding
In this process, a pure graphite or baked carbon rod is used as a non-consumable electrode to create an electric arc between it and the workpiece. The electric arc produces heat and weld can be made with or without the addition of filler material. Carbon arc welding may be classified as-
(1) Single electrode arc welding, and
(2) Twin carbon electrode arc welding
In single electrode arc welding, an electric arc is struck between a carbon electrode and the workpiece. Welding may be carried out in air or in an inert atmosphere. Direct current straight polarity (DCSP) is preferred to restrict electrode disintegration and the amount of carbon going into the weld metal. This process is mainly used for providing heat source for brazing, braze welding, soldering and heat treating as well as for repairing iron and steel castings. It is also used for welding of galvanized steel and copper.
In twin carbon arc welding the arc struck between two carbon electrodes produces heat and welds the joint. The arc produced between these two electrodes heats the metal to the melting temperature and welds the joint after solidification. The power source used is AC (Alternating Current) to keep the electrodes at the same temperature. Twin-electrode carbon arc welding can be used for welding in any position. This process is mainly used for joining copper alloys to each other or to ferrous metal. It can also be used for welding aluminium, nickel, zinc and lead alloys.
Source A Textbook of Basic Manufacturing Processes and Workshop Technology by Rajender Songh.










Post Comment
You must be logged in to post a comment.