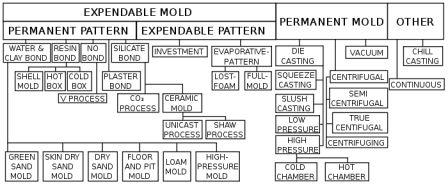
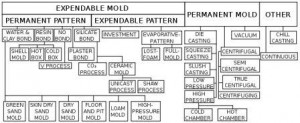
CLASSIFICATION OF MOLDING PROCESSES
Molding processes can be classified in a number of ways. Broadly they are classified either on the basis of the method used or on the basis of the mold material used.
(i) Classification based on the method used
(a) Bench molding.
(b) Floor molding,
(c) Pit molding.
(d) Machine molding.
(ii) Classification based on the mold material used:
(a) Sand molding:
1. Green sand mould
2. Dry sand mould,
3. Skin dried mould.
4. Core sand mould.
5. loam mould
6. Cement bonded sand mould
7. Carbon-dioxide mould.
8. Shell mould.
(b) Plaster molding,
(c) Metallic molding.
(d) Loam molding
Copied from A Textbook of a Basic Manufacturing Processes and Workshop Technology by Rajender Singh.
GREEN SAND CORES
Green sand cores are made by green sand containing moist condition about 5% water and 15- 30 % clay. It imparts very good permeability to core and thus avoids defects like shrinkage or voids in the casting. Green sand cores are not dried. They are poured in green condition and are generally preferred for simple, small and medium castings. The process of making green sand core consumes less time. Such cores possess less strength in comparison to dry sand cores and hence cannot be stored for longer period.
DRY SAND CORES
Dry sand cores are produced by drying the green sand cores to about 110°C. These cores possess high strength rigidity and also good thermal stability. These cores can be stored for long period and are more stable than green sand core. They are used for large castings. They also produce good surface finish in comparison to green sand cores. They can be handled more easily. They resist metal erosion. These types of cores require more floor space, more core material, high labor cost and extra operational equipment. Copied from A Textbook of a Basic Manufacturing Processes and Workshop Technology by Rajender Singh.










Post Comment
You must be logged in to post a comment.