INDUCTION FURNACE and AIR FURNACE
INDUCTION FURNACE
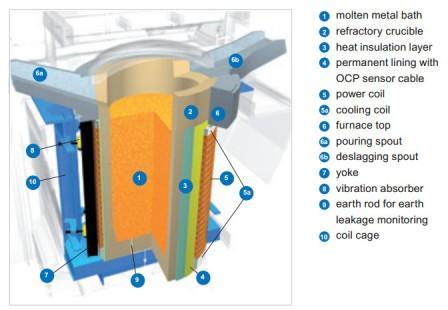
An induction furnace is an electrical furnace in which the heat is applied by induction heating of metal. Induction furnace capacities range from less than one kilogram to one hundred tonnes capacity and are used to melt iron and steel,copper, aluminium and precious metals.
The advantage of the induction furnace is a clean, energy-efficient and well-controllable melting process compared to most other means of metal melting. Most modern foundries use this type of furnace, and now also more iron foundries are replacing cupolas with induction furnaces to melt cast iron, as the former emit lots of dust and other pollutants.
Since no arc or combustion is used, the temperature of the material is no higher than required to melt it; this can prevent loss of valuable alloying elements. The one major drawback to induction furnace usage in a foundry is the lack of refining capacity; charge materials must be clean of oxidation products and of a known composition and some alloying elements may be lost due to oxidation (and must be re-added to the melt). Copied from Wikipedia.
It is also called high frequency induction furnace. It consists of refractory crucible placed centrally inside a water cooled copper coil. Fig. represent the construction and working of this type of furnace.
AIR FURNACE
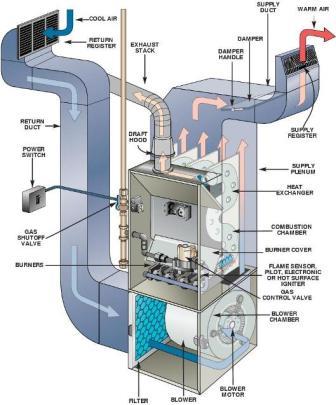
This furnace is also known as puddling or reverbratory furnace. It is used for making wrought iron. Fig shows the construction of this type of furnace. The supply plenum directs air from the central unit to the rooms which the system is designed to heat.
Reference Introduction to basic Manufacturing Processes and Workshop Technology by Rajender Singh.
For engineering project visit this page regularly for know more things related project ideas. Click here to see Ideas of Projects. Engineers Gallery. All the Best!











Post Comment
You must be logged in to post a comment.