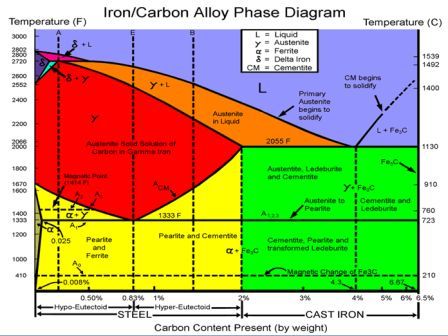
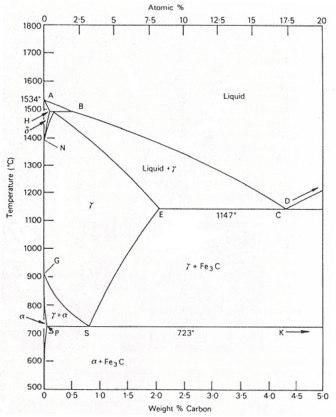
IRON-CARBON EQUILIBRIUM DIAGRAM
Fig. shows, the Fe-C equilibrium diagram in which various structure (obtained during heating and cooling), phases and microscopic constituents of various kinds of steel and cast iron are depicted. The main structures, significance of various lines and critical points are discussed as under.
1. Structures in Fe-C-diagram
The main microscopic constituents of iron and steel are as follows:
1. Austenite
2. Ferrite
3. Cementite
4. Pearlite
1. Austenite
Austenite is a solid solution of free carbon (ferrite) and iron in gamma iron. On heating the steel, after upper critical temperature, the formation of structure completes into austenite which is hard, ductile and non-magnetic. It is able to dissolve large amount of carbon. It is in between the critical or transfer ranges during heating and cooling of steel. It is formed when steel contains carbon up to 1.8% at 1130°C. On cooling below 723°C, it starts transforming into pearlite and ferrite. Austenitic steels cannot be hardened by usual heat treatment methods and are non-magnetic.
2. Ferrite
Ferrite contains very little or no carbon in iron. It is the name given to pure iron crystals which are soft and ductile. The slow cooling of low carbon steel below the critical temperature produces ferrite structure. Ferrite does not harden when cooled rapidly. It is very soft and highly magnetic.
3. Cementite
Cementite is a chemical compound of carbon with iron and is known as iron carbide (Fe3C). Cast iron having 6.67% carbon is possessing complete structure of cementite. Free cementite is found in all steel containing more than 0.83% carbon. It increases with increase in carbon % as reflected in Fe-C Equilibrium diagram. It is extremely hard. The hardness and brittleness of cast iron is believed to be due to the presence of the cementite. It decreases tensile strength. This is formed when the carbon forms definite combinations with iron in form of iron carbides which are extremely hard in nature. The brittleness and hardness of cast iron is mainly controlled by the presence of cementite in it. It is magnetic below 200°C.
4. Pearlite
Pearlite is a eutectoid alloy of ferrite and cementite. It occurs particularly in medium and low carbon steels in the form of mechanical mixture of ferrite and cementite in the ratio of 87:13. Its hardness increases with the proportional of pearlite in ferrous material. Pearlite is relatively strong, hard and ductile, whilst ferrite is weak, soft and ductile. It is built up of alternate light and dark plates. These layers are alternately ferrite and cementite. When seen with the help of a microscope, the surface has appearance like pearl, hence it is called pearlite. Hard steels are mixtures of pearlite and cementite while soft steels are mixtures of ferrite and pearlite.
As the carbon content increases beyond 0.2% in the temperature at which the ferrite is first rejected from austenite drop until, at or above 0.8% carbon, no free ferrite is rejected from the austenite. This steel is called eutectoid steel, and it is the pearlite structure in composition.
As iron having various % of carbon (up to 6%) is heated and cooled, the following phases representing the lines will tell the about the structure of iron, how it charges. Copied from Introduction to Basic Manufacturing Processes and Workshop Technology by Rajender Singh.










Post Comment
You must be logged in to post a comment.