Methods of Hot Extrusion
Hot extrusion process is classified as
1. Direct or forward hot extrusion
2. Indirect or backward hot extrusion
3. Tube extrusion
Different methods of extrusion are shown in Fig. Each method is described as under.
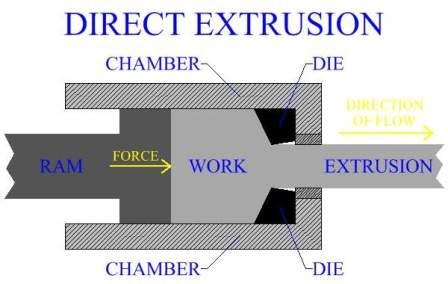
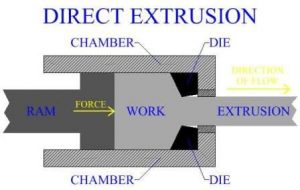
1. Direct or Forward Hot Extrusion
Fig. shows the direct extrusion operational setup. In this method, the heated metal billet is placed in to the die chamber and the pressure is applied through ram. The metal is extruded through die opening in the forward direction, i.e. the same as that of the ram. In forward extrusion, the problem of friction is prevalent because of the relative motion between the heated metal billet and the cylinder walls. To reduce such friction, lubricants are to be commonly used. At lower temperatures, a mixture of oil and graphite is generally used.
The problem of lubrication gets compounded at the higher operating temperatures. Molten glass is generally used for extruding steels.
2. Indirect or Backward Hot Extrusion
Fig. shows the indirect extrusion operational setup. In indirect extrusion, the billet remains stationary while the die moves into the billet by the hollow ram (or punch), through which the backward extrusion takes place. Since, there is no friction force between the billet and the container wall, therefore, less force is required by this method. However this process is not widely used because of the difficulty occurred in providing support for the extruded part.
3. Tube Extrusion
Fig. shows the tube extrusion operational setup. This process is an extension of direct extrusion process where additional mandrel is needed to restrict flow of metal for production of seamless tubes. Aluminium based toothpaste and medicated tubes are produced using this process. Source Introduction of a Basic Manufacturing Processes and Workshop Technology by Rajender Singh.










Post Comment
You must be logged in to post a comment.