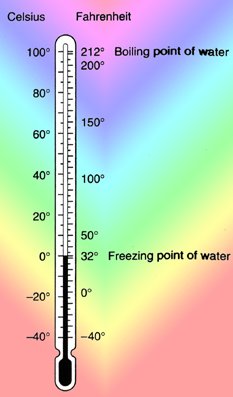
METHODS OF MEASURING TEMPERATURE
Furnace temperature is measured by following methods namely
(1) Electrical pyrometers
(2) Thermo electric pyrometers
(3) Radiation pyrometers
(4) Optical pyrometers and
(5) Photoelectric cells
1) Electrical pyrometers
A pyrometer is a type of remote-sensing thermometer used to measure the temperature of a surface. Various forms of pyrometers have historically existed. In the modern usage, it is a device that from a distance determines the temperature of a surface from the spectrum of the thermal radiation it emits, a process known as pyrometry and sometimes radiometry.
The word pyrometer comes from the Greek word for fire, “πυρ” (pyro), and meter, meaning to measure. The word pyrometer was originally coined to denote a device capable of measuring the temperature of an object by its incandescence, visible light emitted by a body which is at least red-hot. Modern pyrometers or infrared thermometers also measure the temperature of cooler objects, down to room temperature, by detecting their infrared radiation flux.
2) Thermo electric pyrometers
The word pyrometer comes from the Greek word for fire, “πυρ” (pyro), and meter, meaning to measure. The word pyrometer was originally coined to denote a device capable of measuring the temperature of an object by its incandescence, visible light emitted by a body which is at least red-hot.
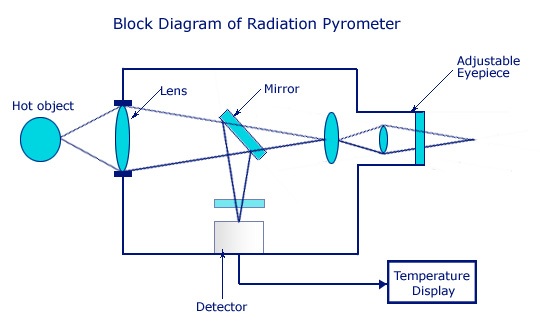
3) Radiation pyrometers
Various forms of pyrometers have historically existed. In the modern usage, it is a device that from a distance determines the temperature of a surface from the spectrum of the thermal radiation it emits, a process known as pyrometry and sometimes radiometry. Modern pyrometers or infrared thermometers also measure the temperature of cooler objects, down to room temperature, by detecting their infrared radiation flux.
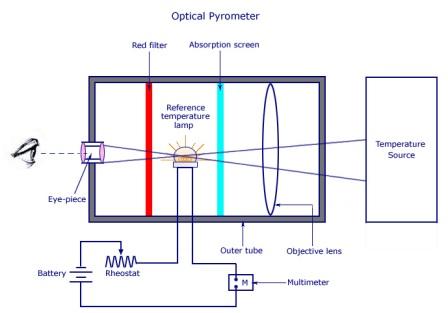
4) Optical pyrometers
The temperature returned by the vanishing filament pyrometer and others of its kind, called brightness pyrometers, is dependent on the emissivity of the object. With greater use of brightness pyrometers, it became obvious that problems existed with relying on knowledge of the value of emissivity. Emissivity was found to change, often drastically, with surface roughness, bulk and surface composition, and even the temperature itself.
5) Photoelectric cells
A solar cell, or photovoltaic cell, is an electrical device that converts the energy of light directly into electricity by the photovoltaic effect, which is a physical and chemical phenomenon. It is a form of photoelectric cell, defined as a device whose electrical characteristics, such as current, voltage, or resistance, vary when exposed to light. Solar cells are the building blocks of photovoltaic modules, otherwise known as solar panels.
Solar cells are described as being photovoltaic irrespective of whether the source is sunlight or an artificial light. They are used as aphotodetector (for example infrared detectors), detecting light or other electromagnetic radiation near the visible range, or measuring light intensity.
Reference Introduction to basic Manufacturing Processes and Workshop Technology by Rajender Singh.
For engineering project visit this page regularly for know more things related project ideas. Click here to see Ideas of Projects. Engineers Gallery. All the Best!










Post Comment
You must be logged in to post a comment.