POWDER METALLURGY
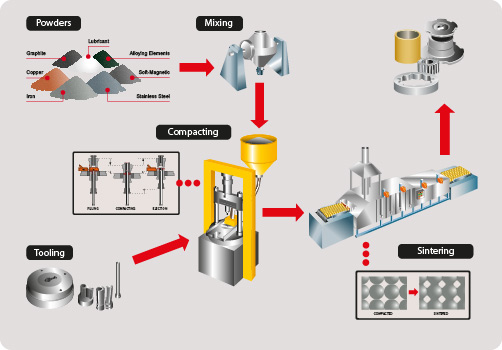
Powder metallurgy is used for manufacturing products or articles from powdered metals by placing these powders in molds and are compacting the same using heavy compressive force. Typical examples of such article or products are grinding wheels, filament wire, magnets, welding rods, tungsten carbide cutting tools, self-lubricating bearings electrical contacts and turbines blades having high temperature strength. The manufacture of parts by powder metallurgy process involves the manufacture of powders, blending, compacting, profiteering, sintering and a number of secondary operations such as sizing, coining, machining, impregnation, infiltration, plating, and heat treatment. The compressed articles are then heated to temperatures much below their melting points to bind the particles together and improve their strength and other properties. Few non-metallic materials can also be added to the metallic powders to provide adequate bond or impart some the needed properties. The products made through this process are very costly on account of the high cost of metal powders as well as of the dies used. The powders of almost all metals and a large quantity of alloys, and nonmetals may be used. The application of powder metallurgy process is economically feasible only for high mass production. Parts made by powder metallurgy process exhibit properties, which cannot be produced by conventional methods. Simple shaped parts can be made to size with high precision without waste, and completely or almost ready for installation. Source Introduction of Basic Manufacturing Processes and Workshop Technology by Rajender Singh.










Post Comment
You must be logged in to post a comment.