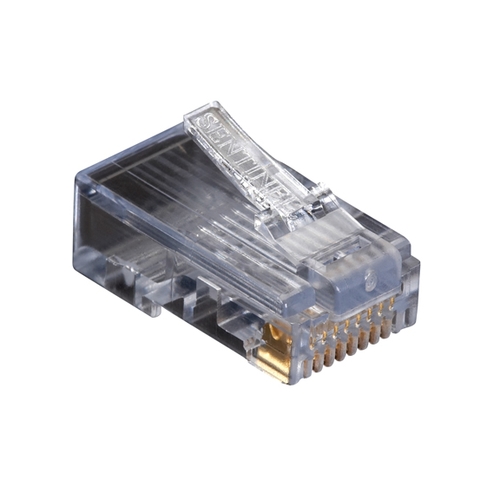
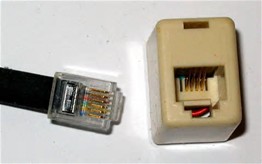
The Registered Jack (RJ) is a connector specifically designed for networking applications. The standard defines only the wiring pattern of the connector, not the geometry or gender. The term ‘Jack’ refers to the female connector even though the standard does not differentiate the gender of the connector. These connectors are also referred to as “modular connectors” as they were helpful in making the telephone network of early days more modular. The RJ standard is primarily defined for the wiring of telephone networks. The connectors following RJ standard wiring pattern are called RJ connector and are available in both male and female types. There is large number of RJ standard connectors available like, RJ11, RJ14, RJ21, RJ45 etc.
The image of a RJ standard female connector
[sam id=”5″ codes=”true”]
The image of a RJ standard male connector
The modular connectors are commonly identified by their ‘contact’ number and their ‘position’ number. The number of contacts refers to the total number of pins in the connector and the number of positions refers to the total number of positions available in which the contacts can be installed in a connector. The number of positions of a connector hence indirectly refers to the actual size of a connector. The modular connectors are defined in four basic sizes, four, six, eight and ten. The 6 position connector with 4 contacts is called 6P4C and an 8 pin connector with 8 contacts is called 8P8C and so on.
Now let us take a look at some of the commonly found RJ connector, their applications and pin-outs.
The pin position of female modular connector from 4 positions to 10 positions is shown in the following figure.
Pin position in female modular connectors












Post Comment
You must be logged in to post a comment.