What is Submersible Pump and How it Works?
A submersible pump (or electric submersible pump (ESP) is a device which has a hermetically sealed motor close-coupled to the pump body. The whole assembly is submerged in the fluid to be pumped.
—A submersible pump is a pump that is able to be placed underwater and still carry out its intended purpose. Some pumps may be designed to work while being fully submerged, whereas others may be submerged or placed in a dry area.
—A submersible water pump pushes water to the surface, instead of sucking the water out of the ground like above ground water pumps..
Submersible series pump is vertically submerged under water and driven by electric. It connects pump body and motor in to a whole one. It is suitable for conveying liquid with slurry, solid particles of gravel, cinders, tailings and groundwater or hot water extraction for irrigation, municipal water use, etc. There many kinds of submersible pump for choose according to different situations for example, some special work may need submersible sewage pump. Inside the motor line packaged with oil-immersed, water immersion and dry-type, check the instructions first before use can not go wrong.
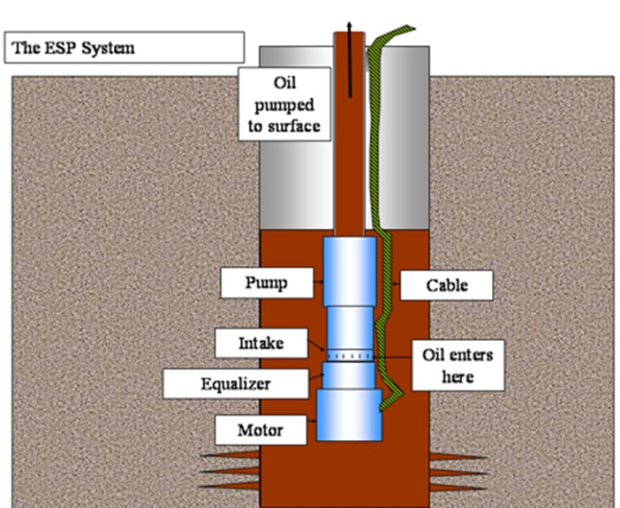
Working Principle
- The submersible pumps used in ESP installations are multistage centrifugal pumps operating in a vertical position. Although their constructional and operational features underwent a continuous evolution over the years, their basic operational principle remained the same.
- —Produced liquids, after being subjected to great centrifugal forces caused by the high rotational speed of the impeller, lose their kinetic energy in the diffuser where a conversion of kinetic to pressure energy takes place.
- The pump shaft is connected to the protector by a mechanical coupling at the bottom of the pump. Well fluids enter the pump through an intake screen and are lifted by the pump stages.
- Other parts include the radial bearings (bushings) distributed along the length of the shaft providing radial support to the pump shaft turning at high rotational speeds.
- An optional thrust bearing takes up part of the axial forces arising in the pump but most of those forces are absorbed by the protector’s thrust bearing.
Applications
- The pump shaft is connected to the protector by a mechanical coupling at the bottom of the pump. Well fluids enter the pump through an intake screen and are lifted by the pump stages.
- Other parts include the radial bearings (bushings) distributed along the length of the shaft providing radial support to the pump shaft turning at high rotational speeds.
- An optional thrust bearing takes up part of the axial forces arising in the pump but most of those forces are absorbed by the protector’s thrust bearing.
- —Efficiency: Compared to the ordinary pumps, the submersible pumps are more efficient as it pumps liquid which is close to the pump. It therefore functions less than the ordinary pumps. As these pumps are placed inside the sumps, it can detect the level of water quite easily.
- —Noise level: The submersible pumps seldom produce less amount of noise as it is submerged under water. The walls of the sump help to soften the sounds caused by the pumps. The ordinary pumps are placed outside the wells or sumps which creates a huge amount of noise.
- —Safe: These pumps are quite safe compared to the other types of pumps as all the potential dangerous components of the pumps are placed under water. It is usually covered and seldom involves the prospects of children tampering with its internal components and valves.
Disadvantages:
- —The largest disadvantage of these pumps is that you put it in the water. This means it will have a shorter life because it is sitting in and sucking up muck from your pond. It is also harder to clean and maintenance because it is sitting on the bottom of the pond.
- —There is the chance the pump will become corroded and lose its seals, thus allowing liquid to penetrate into the motor housing and causing substantial damage to the unit.









Post Comment
You must be logged in to post a comment.