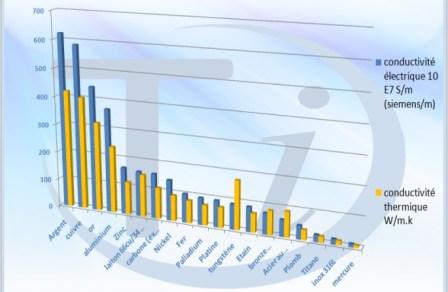
Thermal Properties of Metal
The study of thermal properties is essential in order to know the response of metal to thermal changes i.e. lowering or raising of temperature. Different thermal properties are thermal conductivity, thermal expansion, specific heat, melting point, thermal diffusivity. Some important properties are defined as under.
Melting Point
Melting point is the temperature at which a pure metal or compound changes its shape from solid to liquid. It is called as the temperature at which the liquid and solid are in equilibrium. It can also be said as the transition point between solid and liquid phases.
Melting temperature depends on the nature of inter-atomic and intermolecular bonds. Therefore higher melting point is exhibited by those materials possessing stronger bonds. Covalent, ionic, metallic and molecular types of solids have decreasing order of bonding strength and melting point. Melting point of mild steel is 1500°C, of copper is 1080°C and of Aluminium is 650°C.
It is hard to say something general about the soil thermal properties at a certain location because these are in a constant state of flux from diurnal and seasonal variations. Apart from the basic soil composition, which is constant at one location, soil thermal properties are strongly influenced by the soil volumetric water content, volume fraction of solids and volume fraction of air. Air is a poor thermal conductor and reduces the effectiveness of the solid and liquid phases to conduct heat. While the solid phase has the highest conductivity it is the variability of soil moisture that largely determines thermal conductivity. As such soil moisture properties and soil thermal properties are very closely linked and are often measured and reported together. Temperature variations are most extreme at the surface of the soil and these variations are transferred to sub surface layers but at reduced rates as depth increases. Additionally there is a time delay as to when maximum and minimum temperatures are achieved at increasing soil depth (sometimes referred to as thermal lag).
Reference Introduction to basic Manufacturing Processes and Workshop Technology by Rajender Singh.










Post Comment
You must be logged in to post a comment.