WORM & WORM WHEEL
Worm gears are used when large gear reductions are needed. It is common for worm gears to have reductions of 20:1, and even up to 300:1 or greater.
Many worm gears have an interesting property that no other gear set has: the worm can easily turn the gear, but the gear cannot turn the worm. This is because the angle on the worm is so shallow that when the gear tries to spin it, the friction between the gear and the worm holds the worm in place.
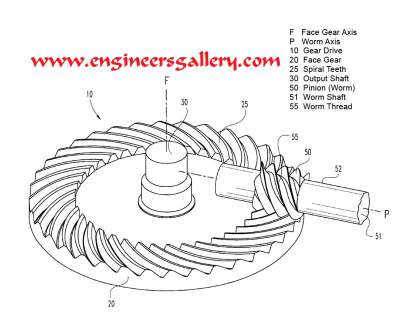
A worm gear (or worm drive) is a specific gear composition in which a screw (worm) meshes with a gear/wheel similar to a spur gear. The set-up allows the user to determine rotational speed and also allows for higher torque to be transmitted. This mechanism can be found in devices both at home and in heavy machinery; the simplest form evident in the tuning mechanism of an acoustic guitar.
What is Worm and Worm Wheel?
- A worm drive is a gear arrangement in which a worm (which is a gear in the form of a screw) meshes with a worm gear (which is similar in appearance to a spur gear, and is also called a worm wheel).
- Like other gear arrangements, a worm drive can reduce rotational speed or allow higher torque to be transmitted. The image shows a section of a gear box with a worm gear being driven by a worm. A worm is an example of a screw, one of the six simple machines.
There are three different types of worm gear:
- Non-throated – this involves a straight worm without a groove machined around the circumference. A single moving point is what provides tooth contact, meaning this particular type of worm gear is subjective to high unit load wear and tear.
- Single-throated – concave helical teeth are wrapped around the worm for line contact, meaning higher unit loads with less excessive wear.
- Double-throated – usually called a cone of hourglass, this type has concave teeth on both the worm screw and the gear itself. Increasing the contact area in such a way allows for increased unit loads with lower wear and tear.
This feature is useful for machines such as conveyor systems, in which the locking feature can act as a brake for the conveyor when the motor is not turning. One other very interesting usage of worm gears is in the Torsen differential, which is used on some high-performance cars and trucks. They are used in right-angle or skew shaft drives. The presence of sliding action in the system even though results in quieter operation, it gives rise to considerable frictional heat, hence they need good lubrication for heat dissipation and for improving the efficiency. High reductions are possible which results in compact drive.
APPLICATION OF WORM GEARS
Worm gears are used widely in
- Tuning Instruments – most guitars, basses, banjos and other stringed instruments use a worm gear for the tuning mechanism to work. The gear’s force reduction is the main reason for this, coupled with the locking capability that keeps the desired string tightness in place. This type of worm gear is different to most as you can tune both up and down; whereas most worm gears can only be turned in one direction.
- Elevators/Lifts – worm gears can often be found in the machinery of common elevators/lifts because of their compact size and non-reversible properties. As the gear/load cannot transmit motion back through the worm/hoist, using this type of gear can act as a secondary braking system. This means the load cannot free fall and load speed is easily regulated.
- Torsen Differentials – Large trucks or off-road vehicles, such as the Hummer, often need to deliver different amounts of torque to the each wheel, depending on what action the vehicle is performing. For example, wheels need to spin at different speeds whilst turning a corner as the inside wheels travel a shorter distance. A vehicle’s Torsen differential will handle this movement via a combination of worms and worm gears that separate each individual wheel’s performance.
- Gates and Conveyor Belts – Typical worm drives can only be turned in one direction, which means that conveyor belts and security gates lock-up when not being used and will not run backwards. Automatic security gates will often adopt two worm drives, one to open and another to close. This means the gate can be locked in each direction and cannot be breached or forced.
- Worm gear drives operate silently and smoothly.
- They are self-locking.
- They occupy less space.
- They have good meshing effectiveness.
- They can be used for reducing speed and increasing torque.
- High velocity ratio of the order of 100 can be obtained in a single step.
- Worm gear materials are expensive.
- Worm drives have high power losses.
- A disadvantage is the potential for considerable sliding action, leading to low efficiency.
- They produce a lot of heat.












Post Comment
You must be logged in to post a comment.