Hooke’s law* states that when a material is loaded within elastic limit, the stress is directly proportional to strain,
i.e.
σ ∝ε or σ = E.ε
∴ E = σ/ε = (P× l)/(A×δl)
Where, E is a constant of proportionality known as Young’s modulus or modulus of elasticity. In S.I. units, it is usually expressed in GPa i.e. GN/m2 or kN/mm2. It may be noted that Hooke’s law holds good for tension as well as compression.
The following table shows the values of modulus of elasticity or Young’s modulus (E) for the materials commonly used in engineering practice.
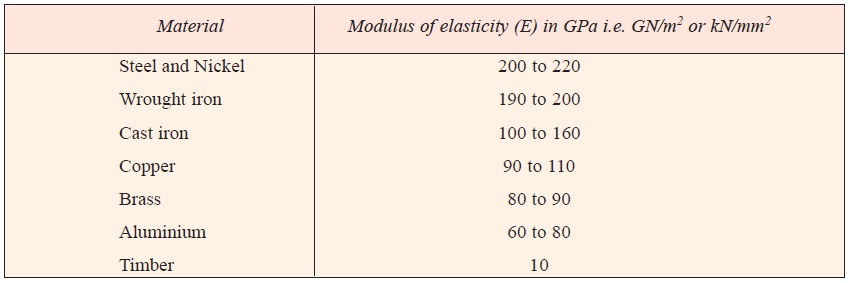
Reference
A textbook of Machine Design by R.S.Khurmi and J.K.Gupta










Post Comment
You must be logged in to post a comment.