COMPRESSIVE STRESS AND STRAIN
When a body is subjected to two equal and opposite axial pushes P (also called compressive load) as shown in Fig. 2 (a), then the stress induced at any section of the body is known as compressive stress as shown in Fig. 2(b). A little consideration will show that due to the compressive load, there will be an increase in cross-sectional area and a decrease in length of the body. The ratio of the decrease in length to the original length is known as compressive strain.
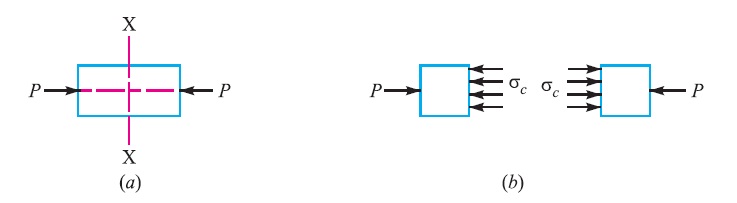
Let, P = Axial compressive force acting on the body,
A = Cross-sectional area of the body,
l = Original length, and
δl = Decrease in length.
∴ Compressive stress, σc = P/A
and Compressive strain, εc = δl /l
Note : In case of tension or compression, the area involved is at right angles to the external force applied.
Reference
A textbook of Machine Design by R.S.Khurmi and J.K.Gupta