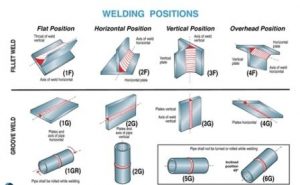
Welding Positions
As shown in Fig., there are four types of welding positions, which are given as:
1. Flat or down hand position
2. Horizontal position
3. Vertical position
4. Overhead position
1. Flat or Downhand Welding Position
The flat position or down hand position is one in which the welding is performed from the upper side of the joint and the face of the weld is approximately horizontal. This is the simplest and the most convenient position for welding. Using this technique, excellent welded joints at a fast speed with minimum risk of fatigue to the welders can be obtained.
2. Horizontal Welding Position
In horizontal position, the plane of the workpiece is vertical and the deposited weld head is horizontal. The metal deposition rate in horizontal welding is next to that achieved in flat or downhand welding position. This position of welding is most commonly used in welding vessels and reservoirs.
3. Veritical Welding Position
In vertical position, the plane of the workpiece is vertical and the weld is deposited upon a vertical surface. It is difficult to produce satisfactory welds in this position due to the effect of the force of gravity on the molten metal. The welder must constantly control the metal so that it does not run or drop from the weld. Vertical welding may be of two types viz., vertical-up and vertical-down. Vertical-up welding is preferred when strength is the major consideration. The vertical-down welding is used for a sealing operation and for welding sheet metal.
4. Overhead Welding Position
The overhead position is probably even more difficult to weld than the vertical position. Here the pull of gravity against the molten metal is much greater. The force of the flame against the weld serves to counteract the pull of gravity. In overhead position, the plane of the workpiece is horizontal. But the welding is carried out from the underside. The electrode is held with its welding end upward. It is a good practice to use very short arc and basic coated electrodes for overhead welding. Source A Textbook of Basic Manufacturing Processes and Workshop Technology by Rajender Songh.